Whether you’re driving a new energy vehicle with smooth acceleration, using an inverter air conditioner to adjust the room temperature, or watching a photovoltaic power station convert solar energy into household electricity, the core of power conversion is essential behind the scenes—the IGBT module. As a crucial component in power electronics, it not only bridges direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC), but also underpins the efficient operation of everything from everyday appliances to industrial equipment, rail transit, and new energy systems. However, most people know little about the principles, components, and applications of this “invisible hero.” This article will begin with a definition of the IGBT, then break down its core components, operating mechanisms, and key advantages. It will also outline its various application environments and introduce the technical features of major global manufacturers to help you fully understand this crucial component that impacts modern power systems.
1. What is an IGBT?
IGBT, short for Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor, is a three-terminal power semiconductor device (gate G, collector C, and emitter E) at the heart of the power electronics industry. Its core value lies in its ability to function as an efficient and controllable electronic switch. It innovatively combines the high input impedance of metal-oxide semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) (for low-voltage control) with the high current-carrying capacity of bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) (for high power applications). This enables nanosecond-scale current switching, resulting in significantly lower switching losses than traditional power devices. This makes it a key choice for today’s high-power electronic devices, such as new energy vehicle inverters and industrial frequency converters.
In practical applications, the power, heat dissipation, and stability of a single IGBT chip are insufficient to meet complex requirements, leading to further integration into IGBT power modules. These modules are not simply a physical package of multiple IGBT power semiconductor chips. Instead, they utilize a systematic design to integrate the IGBT chip, freewheeling diode (to suppress reverse voltage spikes during turn-off), gate drive auxiliary circuitry, and even basic protection components (such as overcurrent detection) within a single insulated package. Furthermore, the use of high-thermal-conductivity materials such as ceramic substrates significantly increases the module’s overall power density while optimizing heat transfer efficiency, ensuring reliability under high loads and long-term operation.
2. Core Components of IGBT
- A single IGBT module is an integrated functional unit designed for high power. It integrates core components into a rugged and insulated package (commonly made of epoxy molding compound and a ceramic substrate, ensuring both heat resistance and insulation). Each component has a clear division of labor and works together to ensure stable module operation:
- IGBT chip: The “power core” of the module, responsible for the precise switching of high-power currents. As a hybrid semiconductor device combining a MOSFET and a bipolar junction transistor (BJT), it combines the high input impedance of a MOSFET (facilitating low-voltage control) with the high current-carrying capacity of a BJT (accommodating high currents), making it the foundation for efficient power conversion.
- Freewheeling diode: Also known as an “anti-parallel diode,” it is connected in anti-parallel with the IGBT chip. When the IGBT is turned off, the reverse induced electromotive force generated by inductive loads in the circuit (such as motors) generates a high-voltage spike. The freewheeling diode provides a reverse current path, preventing the spike from breaking down the chip and smoothing the current waveform, ensuring stable system operation. Gate driver: The module’s “control center,” connecting low-voltage control signals to the high-voltage IGBT chip. By outputting appropriate voltage (typically +12V to +15V for on-state switching, -5V to 0V for off-state switching) and current to the gate, it ensures fast and stable IGBT switching, preventing chip malfunction or damage due to abnormal drive signals.
- Protection: The module’s “safety barrier.” Most products feature built-in overcurrent, overtemperature, and short-circuit protection. When excessive current, excessive temperature, or a short circuit is detected, the drive signal is quickly cut off to prevent module damage. Some industrial-grade modules also integrate undervoltage protection for further reliability.
- Heat sink/cooling system: The module’s “temperature control unit,” designed to mitigate the conduction and switching losses generated by the IGBT. Heat is conducted internally through a high-thermal-conductivity ceramic substrate, while the outside is equipped with aluminum heat sink fins (suitable for small and medium power), or a reserved liquid cooling interface (suitable for high power, such as new energy vehicle inverters), to ensure that the module operating temperature is stable within a safe range (≤125°C junction temperature), avoiding overheating that affects performance and life.
3. What is its working principle of IGBT?
The core operating logic of an IGBT module is to act as a “controllable electronic switch,” precisely controlling the on-off flow of current to achieve bidirectional conversion between direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC). Its operation relies on voltage-controlled current flow, offering both high speed and high efficiency.
This process is voltage-controlled: a small voltage applied to the gate terminal controls a larger current flowing between the collector and emitter terminals. It is precisely this high-speed and efficient power conversion capability that makes IGBT modules a core component in high-power systems such as electric motor drives (such as those in new energy vehicles) and inverters (such as photovoltaic inverters), ensuring stable conversion between different power modes and supporting the normal operation of equipment.
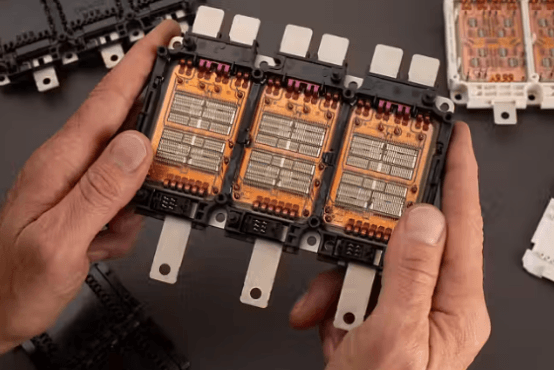
4. What Are the Main Advantages of IGBT?
IGBT power modules are highly favored in high-power applications for the following reasons:
- High Efficiency: They significantly reduce power losses (such as conduction and switching losses) during operation. This is crucial for improving overall energy efficiency in energy-efficient systems such as new energy and industrial applications.
- High Power Density: By integrating multiple components into an integrated package, high power output is achieved in a compact size, effectively saving installation space and making them suitable for size-sensitive applications such as new energy vehicles and small inverters.
- High Reliability: The integrated design not only simplifies external assembly but also reduces failure risk and improves long-term operational stability through built-in thermal management structures (such as ceramic substrates) and protection features (overcurrent and overtemperature).
- High Voltage/Current Rating: They can withstand high voltages up to 6.5kV and high currents of hundreds of amperes, easily meeting the power demands of heavy-duty applications such as industrial motor drives and rail transit.
5. What is the function of IGBT power modules?
An IGBT power module is essentially a highly efficient electronic switch. Its core value lies in building a “conversion bridge” between direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC). It can convert DC to AC and vice versa, meeting the diverse power requirements of various electronic devices.
Let’s use an everyday analogy: Imagine you have an outdoor power supply that outputs DC power and want to power a small projector that requires AC. The current direction of the outdoor power supply is always fixed. Using a conventional switch to repeatedly switch it on and off would only produce intermittent DC pulses, which is incapable of powering the projector. To generate the alternating AC power required by the projector, a switch that can precisely reverse the current direction is required, requiring approximately 100 switching cycles per second—equivalent to 6,000 adjustments per minute. Conventional switches simply cannot withstand this high frequency of operation, but IGBT power modules can perform this task stably and efficiently.
This power conversion capability is a crucial component of the normal operation of numerous devices. For example, automobile drive motors and large motors in industrial production lines all require three-phase AC power to operate; however, electric vehicle power batteries and household energy storage batteries store DC power. It is the conversion function of the IGBT module that smoothly “transforms” the DC power stored in the battery into the AC power required by the motor, allowing the energy generated by the motor to be recharged back into the DC battery. Without it, there would be an “energy gap” between DC energy storage devices and AC appliances, making scenarios like new energy vehicle driving, grid-connected photovoltaic power plants, and household inverter appliances impossible.
6. Where are IGBTs Used?
IGBTs have a wide range of applications, covering everything from everyday appliances and industrial production to new energy, transportation, and specialized applications. They play a core role in power electronics systems:
- Electric vehicles (EVs): This is both a widespread application and a core application of modern power electronics systems. They are used in powertrains to convert DC power from batteries into AC power to power the motor.
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): As a typical application of IGBTs, they are widely applicable to various devices requiring motor speed regulation, supporting energy-saving operation in the industrial and home appliance sectors.
- Lamp Ballasts: Leveraging the current control capabilities of IGBTs, they stabilize lamp power supply and improve luminous efficiency, meeting the needs of various lighting equipment.
- Air Conditioners: Utilizing IGBTs to regulate compressor speed, air conditioners achieve variable frequency operation, balancing cooling and heating performance with energy consumption, a common household appliance application.
- Renewable Energy: They play a crucial role in modern power electronics systems, specifically in solar and wind power systems, acting as inverters to convert DC power into AC power for transmission to the grid.
- Industrial Motor Drives: As core components, they control the speed and torque of large motors in manufacturing and automation, ensuring precision and efficiency in industrial production.
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPSs): They provide reliable backup power for sensitive equipment such as servers and medical devices, a crucial application for ensuring continuous operation.
- Railway and Transportation: They power the high-voltage traction systems of electric trains, supporting the stable operation of rail transit and are a core application in the transportation sector. Military Applications and High-Speed Current Switching Devices: These devices play a role in military applications and nearly all electronic devices requiring high-speed current switching, meeting specialized precision power control requirements.
7. What are the world’s leading IGBT manufacturers, and what are their strengths and core technological highlights?
- Infineon Technologies (Germany): Leading global IGBT market share, covering all applications and leading in automotive-grade 800V modules.
- Mitsubishi Electric (Japan): A leader in high-voltage, high-power technology, a benchmark for rail transit and photovoltaic inverter modules.
- Semikron (Germany): A benchmark in industrial motor drive technology, with high-weather-resistant modules favored by the top 10 inverter manufacturers.
- Fuji Electric (Japan): A leader in the home appliance and consumer electronics industry, with over 40% market share in IPM modules (serving Midea and Gree).
- ON Semiconductor (USA): Developing a dual-track approach with SiC and IGBTs, with automotive-grade SiC modules being mass-produced for Tesla.
- STMicroelectronics (Europe): The price-performance leader in industrial consumer electronics, offering low-cost modules and integrated automotive BMS solutions.
- Star Semiconductor (China): Leading domestic automotive-grade IGBT market share (28% in 2024), with SiC production line yield exceeding 75%.
From definition to application, from technological advantages to manufacturer landscape, the value of IGBT modules has long permeated every aspect of modern life and industrial production. It’s not only the “heart” of new energy vehicle powertrains, but also the “power regulator” of industrial automation equipment and the driving force behind energy transition. For companies adapting to diverse scenarios, selecting the right IGBT module not only impacts device performance but also the energy efficiency and reliability of their products.
7SE, with years of experience in the electronic components industry, consistently tracks the technological trends of major global IGBT manufacturers. We currently offer a wide range of IGBT modules, covering automotive, industrial, and consumer grades. Whether adapting to standard models from international brands like Infineon and Mitsubishi, or matching cost-effective modules from domestic manufacturers like Star Semiconductor, we provide industry-standard products and technical consulting services tailored to the voltage and current requirements of various application industries (such as new energy, industrial automation, and home appliance manufacturing), enabling partners to rapidly adapt to R&D and production schedules. As wide-bandgap technologies like SiC advance, we will continue to enhance our supply chain to help partners quickly respond to technology upgrades and seize development opportunities in the power electronics sector.
